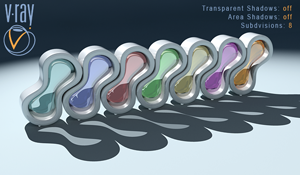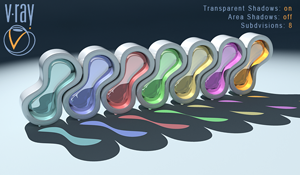
Transparent Shadows: on , Area Shadows: off
Subdivisions: 8
With these settings the VRayShadow acts like a Raytraced Shadow. In this case the Subdivisions have no effect on the final result. Notice that VRayShadow takes in concern only the geometry of the objects and the transparency of their materials (we have colored shadows).